Ubuntu EE GPU Installation With Tarball
| Note | MapD has been rebranded to OmniSci. |
This is an end-to-end recipe for installing OmniSci Enterprise Edition on an Ubuntu machine running with NVIDIA Kepler or Pascal series GPU cards. This install has all of the functionality of OmniSci.
Here is a quick video overview of the installation process.
- The installation phases are:
Note: The order of these instructions is significant. Please install each component in the order presented to prevent aggravated hair loss.
Assumptions
- These instructions assume the following:
- You are installing on a “clean” Ubuntu host machine with only the operating system installed.
- Your OmniSci host only runs the daemons and services required to support OmniSci.
- Your OmniSci host is connected to the Internet.
Preparation
Prepare your Ubuntu machine by updating your system, creating the OmniSci user (named mapd), installing kernel headers, installing CUDA drivers, and enabling the firewall.
Update and Reboot
- Update the entire system:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
- Install a “headless” Java Runtime Environment:
sudo apt install default-jre-headless
- Verify that the
apt-transport-httpsutility is installed:sudo apt install apt-transport-https
- Reboot to activate the latest kernel:
sudo reboot
Create the OmniSci User
Create a group called mapd and a user named mapd, who will be the owner of the OmniSci database. You can create both the group and user with the useradd command and the -U switch.
sudo useradd -U mapd
Install CUDA Drivers
CUDA is a parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) model. It uses a CUDA-enabled graphics processing unit (GPU) for general purpose processing. The CUDA platform provides direct access to the GPU virtual instruction set and parallel computation elements. For more information on CUDA unrelated to installing OmniSci, see http://www.nvidia.com/object/cuda_home_new.html.
Install Kernel Headers
- Identify the Linux kernel you are using by issuing the
uname -rcommand. - Use the name of the kernel (
4.15.0-1021-awsin the following code example) to install kernel headers and development packages:sudo apt-get install linux-headers-4.15.0-1021-aws
- Reboot to ensure that the kernel is up to date:
sudo reboot
Install the Drivers
OmniSci requires only the CUDA drivers and not the entire CUDA package. To install the drivers:
- Go to https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads.
- Select the target platform by selecting the operating system (Linux), architecture (based on your environment), distribution (Ubuntu), version (based on your environment), and installer type (OmniSci recommends deb (network)).
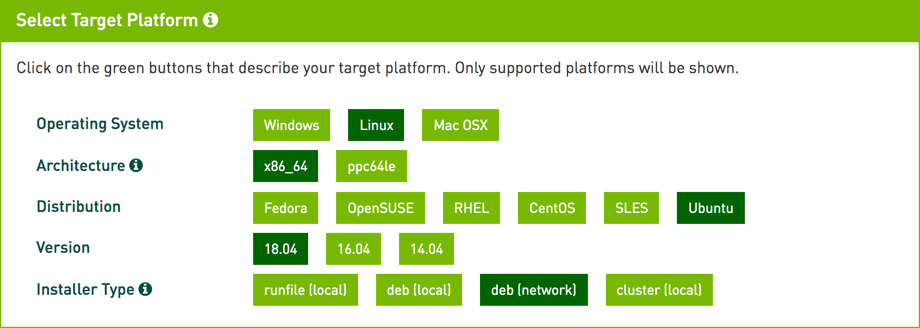
- In Download Installer..., right-click the Download button and copy the link location of the Base Installer. Do not use the installation instructions on the CUDA site.

- Use one of the following methods to download the installer from the command line, using the download link you copied (in this example, https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu1804/x86_64/cuda-repo-ubuntu1804_10.0.130-1_amd64.deb):
curl:sudo curl -O https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu1804/x86_64/cuda-repo-ubuntu1804_10.0.130-1_amd64.deb
wget:sudo wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu1804/x86_64/cuda-repo-ubuntu1804_10.0.130-1_amd64.deb
If
wgetis not installed in your environment, usesudo apt install wgetto install it.
- Install the CUDA drivers, using the filename you just downloaded (in this example, cuda-repo-ubuntu1804_10.0.130-1_amd64.deb):
sudo dpkg -i <file_name>
- If you do not have the public CUDA GPG key installed, run the installation command provided by NVIDIA in the terminal window; for example:
sudo apt-key adv --fetch-keys http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu1804/x86_64/7fa2af80.pub
- Update the local repository cache:
sudo apt update
- Install the CUDA Toolkit and GPU drivers:
sudo apt install cuda-drivers linux-image-extra-virtual
- Reboot your system to ensure that all changes are active:
sudo reboot
Checkpoint
Run nvidia-smi to verify that your drivers are installed correctly and recognize the GPUs in your environment. Depending on your environment, you should see something like this to verify that your NVIDIA GPUs and drivers are present: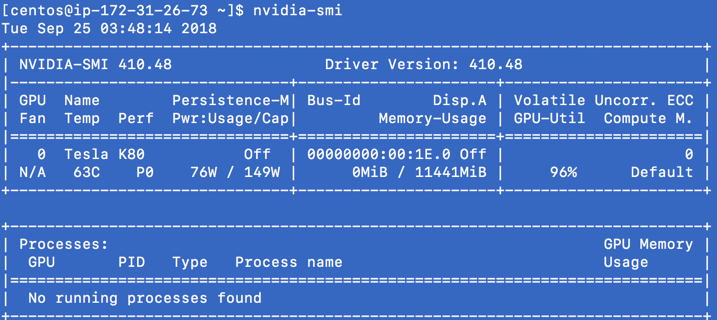
| Note | If you see an error like the following, the NVIDIA drivers are probably installed incorrectly:
NVIDIA-SMI has failed because it couldn't communicate with the NVIDIA driver. Make sure that the latest NVIDIA driver is installed and running.Review the Install CUDA Drivers section and correct any errors. |
Enable the Firewall
To use Immerse, you must prepare your host machine to accept HTTP connections. You can configure your firewall for external access.
sudo ufw disable
sudo ufw allow 9092/tcp
sudo ufw allow ssh
sudo ufw enableFor more information, see https://help.ubuntu.com/lts/serverguide/firewall.html.
| Note | Most cloud providers provide a different mechanism for handling firewall configuration. The commands above might not run in cloud deployments. |
Installation
You install the OmniSci application itself by expanding a TAR file.
- Create an
installsdirectory in your home folder:cd ~ sudo mkdir installs cd installs
- Download the desired version of OmniSci from the URL provided you by your Account Executive.
- Expand the OmniSci archive file in the
installsdirectory with the following command:sudo tar -xvf <file_name>.tar.gz
- List the contents of the
installsdirectory and copy the name of the directory created when expanding the archive. For example:mapd-ee-4.3.0-20181119-b7f85d00bd-Linux-x86_64-render
- Go to the
optfolder and create a symbolic link to the directory you just copied:cd /opt ln -s ~/installs/<onmisci_directory> mapd
Configuration
Follow these steps to prepare your OmniSci environment.
Set Environment Variables
For convenience, you can update .bashrc with the required environment variables.
- Open a terminal window.
- Enter
cd ~/to go to your home directory. - Open
.bashrcin a text editor. For example,sudo gedit .bashrc. - Edit the
.bashrcfile. Add the following export commands under “User specific aliases and functions.”# User specific aliases and functions export MAPD_USER=mapd export MAPD_GROUP=mapd export MAPD_STORAGE=/var/lib/mapd export MAPD_PATH=/opt/mapd export MAPD_LOG=/var/lib/mapd/data/mapd_log
- Save the
.bashrcfile. - Open a new terminal window to use your changes.
The $MAPD_STORAGE directory must be dedicated to OmniSci: do not set it to a directory shared by other packages.
Initialization
Run the systemd installer. This script requires sudo access. You
might be prompted for a password.
cd $MAPD_PATH/systemd sudo ./install_mapd_systemd.sh
You are prompted for two paths during install: MAPD_PATH and MAPD_STORAGE. MAPD_PATH must be the same as the location of the symbolic link you created in step 5 of the installation process and the environment variable you just created. In a standard installation, that path is /opt/mapd. MAPD_STORAGE defaults to /var/lib/mapd.
The script creates a data
directory in $MAPD_STORAGE with the directories mapd_catalogs,
mapd_data, and mapd_export. mapd_import and mapd_log
directories are created when you insert data the first time. The mapd_log
directory is of particular interest to OmniSci administrators.
Activation
Start and use OmniSci Core and Immerse.
Start OmniSci Core
cd $MAPD_PATH sudo systemctl start mapd_server sudo systemctl start mapd_web_server
Enable OmniSci Core to start when the system reboots.
sudo systemctl enable mapd_server sudo systemctl enable mapd_web_server
Checkpoint
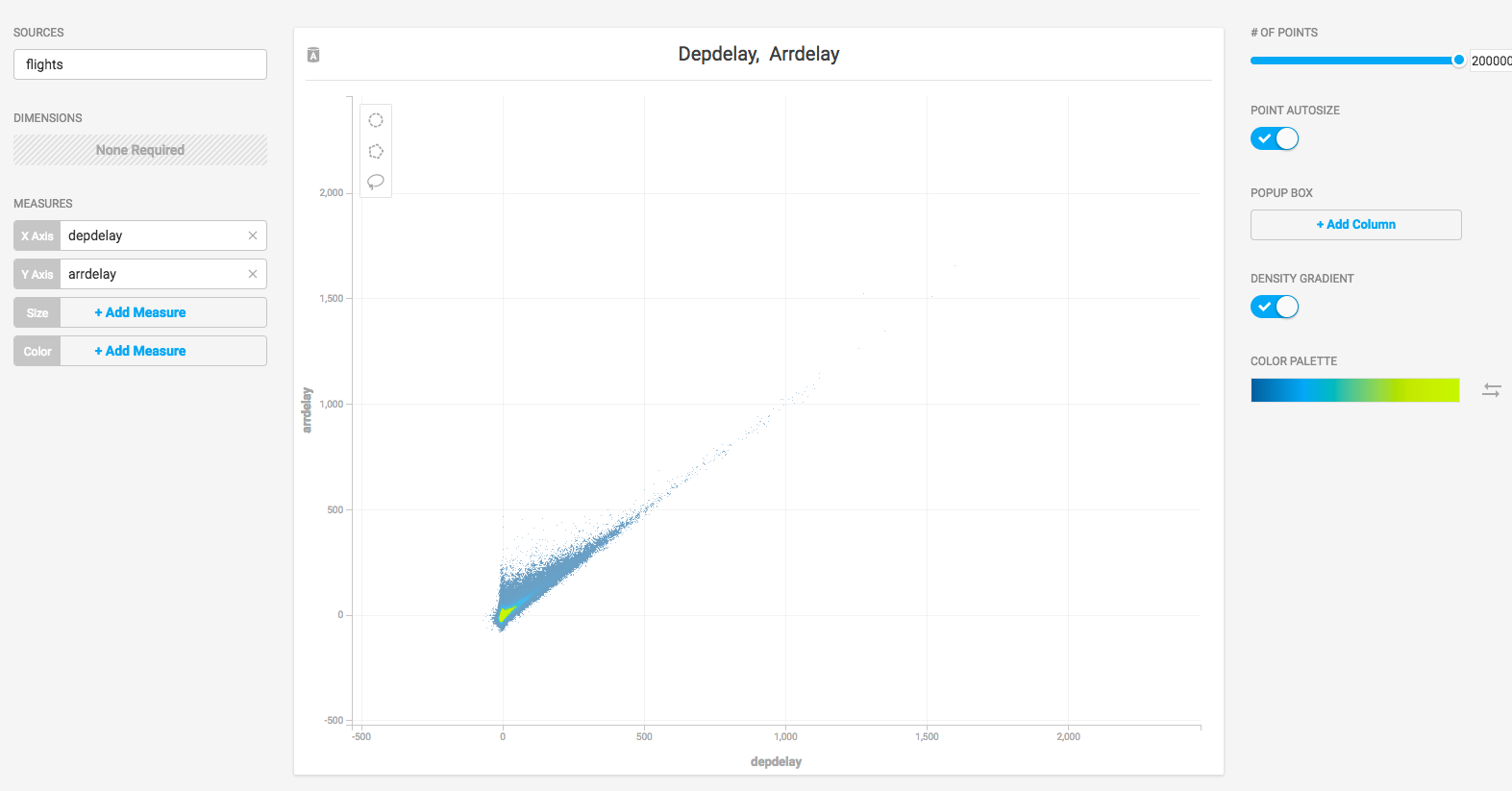
To verify that everything is working correctly, load some sample data, perform a mapdql query, and generate a pointmap using Immerse.
- OmniSci ships with two sample datasets of airline flight information collected in 2008. To install the sample data, run the following command.
cd $MAPD_PATH sudo ./insert_sample_data
- When prompted, choose whether to insert dataset 1 (7 million rows) or dataset 2 (10 thousand rows).
Enter dataset number to download, or 'q' to quit: # Dataset Rows Table Name File Name 1) Flights (2008) 7M flights_2008_7M flights_2008_7M.tar.gz 2) Flights (2008) 10k flights_2008_10k flights_2008_10k.tar.gz
- Connect to OmniSci Core by entering the following command in a terminal on the host machine (default password is HyperInteractive):
$MAPD_PATH/bin/mapdql password: ••••••••••••••••
- Enter a SQL query such as the following, based on dataset 2 above:
mapdql> SELECT origin_city AS "Origin", dest_city AS "Destination", AVG(airtime) AS "Average Airtime" FROM flights_2008_10k WHERE distance < 175 GROUP BY origin_city, dest_city; Origin|Destination|Average Airtime Austin|Houston|33.055556 Norfolk|Baltimore|36.071429 Ft. Myers|Orlando|28.666667 Orlando|Ft. Myers|32.583333 Houston|Austin|29.611111 Baltimore|Norfolk|31.714286
- Connect to Immerse using a web browser connected to your host machine on port 9092. For example,
http://omnisci.mycompany.com:9092. - Create a new dashboard and a Scatter Plot to verify that backend rendering is working.
- Click New Dashboard.
- Click Add Chart.
- Click SCATTER.
- Click Add Data Source.
- Choose the flights_2008_10k or flights_2008_7M table as the data source, depending on the dataset you selected for ingest.
- Click X Axis +Add Measure.
- Choose depdelay.
- Click Y Axis +Add Measure.
- Choose arrdelay.